Japan's Cold Chain Ecosystem: How Invisible Technology Preserves Food Freshness and Reduces Waste
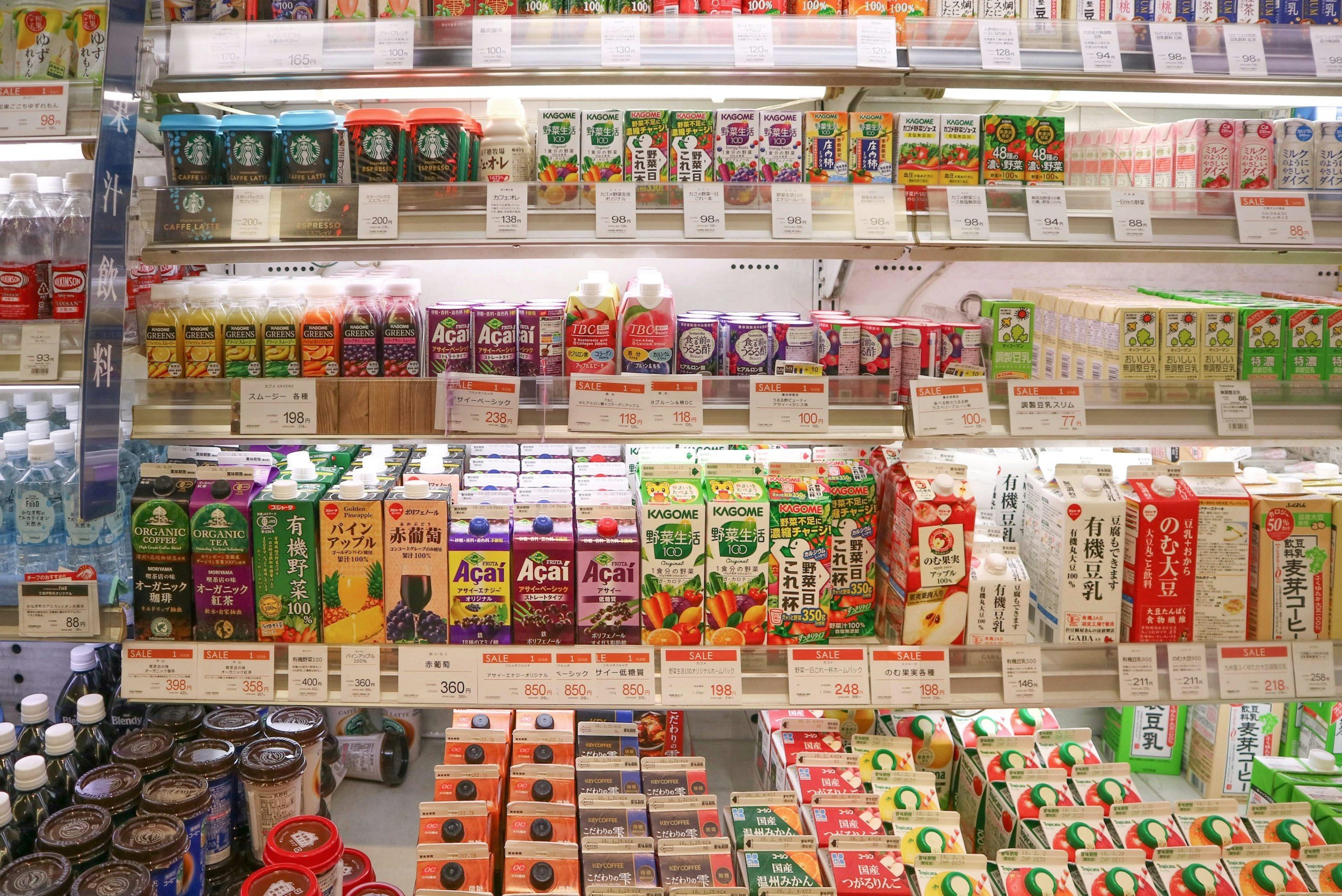
Japan possesses a sophisticated "invisible technology ecosystem" within its cold chain that enables convenience stores to maintain a food waste rate of merely 2 per cent. Driven by a cultural obsession with freshness and high urban density, this system integrates advanced packaging, multi-temperature logistics, and AI-driven inventory management. Whilst Western retailers often grapple with much higher spoilage, Japan’s integrated approach offers a proven model for simultaneously enhancing quality and profitability.
An Explanation of the Licensing Structure of Anime Figurines – Who is the Rightsholder?
Japan's anime figurine licensing structure operates through three distinct layers—original work rights, anime adaptation rights, and merchandising rights—each held by different parties and requiring separate contracts. This complexity stems from the country's production committee system, where multiple companies jointly invest hundreds of millions of yen in anime production and recoup costs through merchandise licensing. Understanding which design materials to use determines the contracting party: original manga art requires publisher agreements, whilst anime character designs necessitate production committee contracts.
Why Japan's Caregiving Assistance Technology Deserves Attention Now: Leadership in ISO Standards and the Strength of Field-Oriented Development
Japan's caregiving assistance technology merits attention now, underpinned by a three-layered competitive edge forged over a decade ahead of Asia's ageing crisis. It leads in crafting global safety standards whilst institutionalising field-tested development that yields intuitive usability. Precision components, with world-leading shares in compact, high-torque designs, sustain this prowess, positioning Japan advantageously amid intensifying international rivalry.
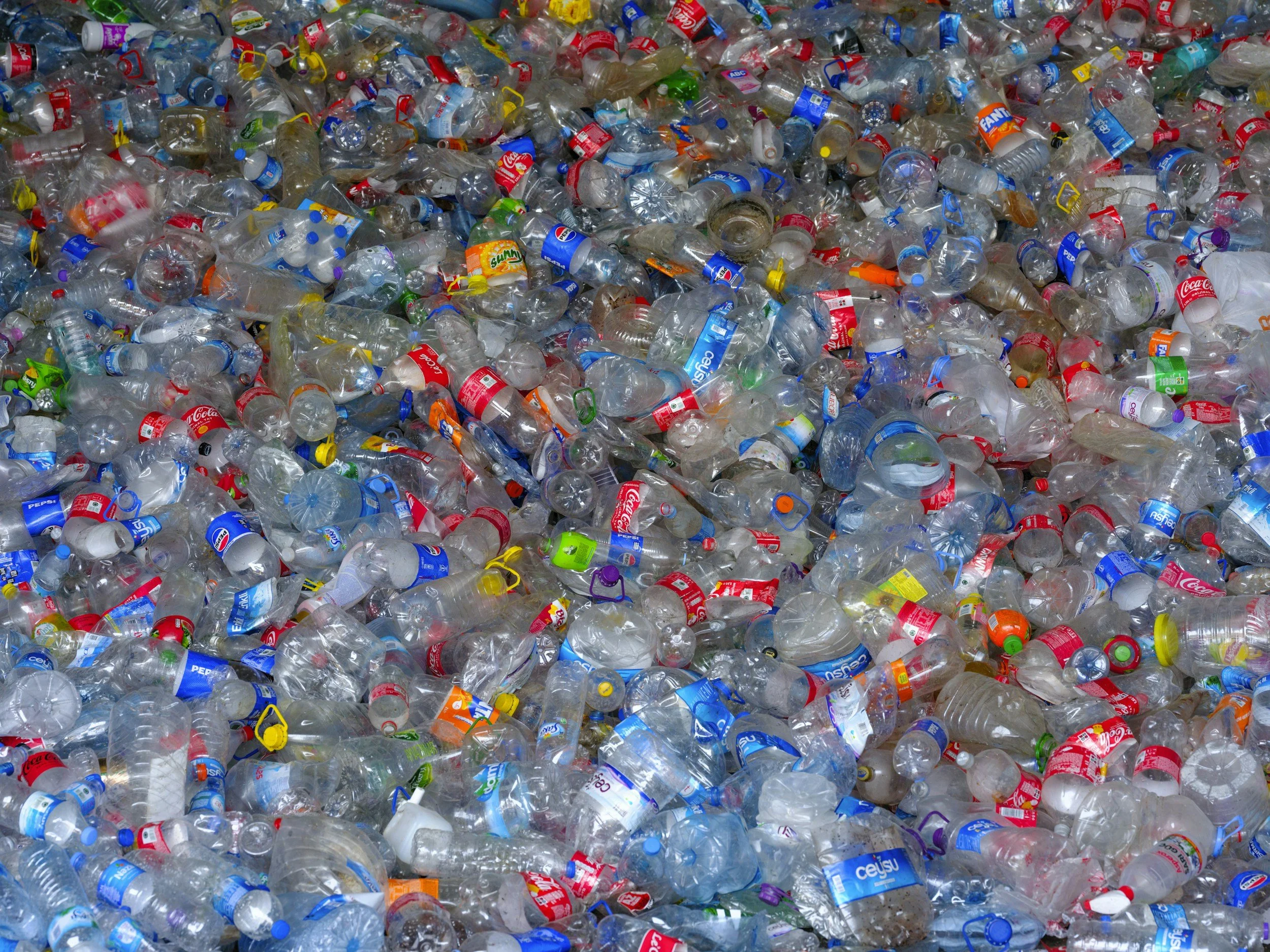
Japan's Waste Recycling Technology: A Circular System Transforming 'Rubbish' into Resources
Japan's small and medium recycling enterprises are transforming waste plastics and organic materials into exportable resources through precision sorting technologies and quality management systems. Underpinned by the country's circular society framework established in 2000, these firms supply recycled materials meeting international standards to global manufacturers. Whilst competing against rising capabilities in China and Southeast Asia, Japanese recyclers maintain competitive advantage through traceability, stable quality, and niche technical expertise that appeal to overseas buyers seeking sustainable supply chains.
Japanese Noise Control Technology: How Small and Medium-Sized Enterprises Are Transforming Infrastructure Markets with Custom Solutions
Japanese small and medium-sized enterprises are transforming the global noise control market through customised solutions that address site-specific challenges which standardised mass-produced products cannot solve. With patented lightweight aluminium technologies achieving high performance across 500 to 2,000 Hz whilst using over 95% recyclable materials, companies with merely 20 employees supply major corporations including automotive and power generation firms. Their field-oriented design capability, in-house integrated production, and turnkey service from consultation to after-sales support offer effective solutions for the 1 billion people worldwide exposed to harmful noise levels.
Japan's Competitive Edge in Beauty Device Manufacturing: Quality and Safety Underpinned by the Hidden Strength of 'Intermediate Materials'
Japan's beauty device industry maintains global competitiveness not through final product assembly, but through dominance in 'invisible' intermediate materials. High-performance resins, medical-grade polymers, specialised synthetic rubbers, and precision electronic components supplied by Japanese chemical and materials manufacturers underpin the safety, durability, and performance that define 'Made in Japan' quality. This mirrors the semiconductor industry, where Japan commands 50 to 90 per cent of global market share in manufacturing materials despite losing dominance in chip production. The advantage stems from decades of accumulated research and development, rigorous quality control culture, and sophisticated industry-academia collaboration that competitors cannot easily replicate.
Japanese Packaging Technology: Reconciling Environmental Responsibility with Functionality
Japan's packaging industry has mastered the difficult balance between environmental responsibility and advanced functionality. Through stringent regulations including the Food Sanitation Act's positive list system and comprehensive traceability, Japanese manufacturers deliver materials that simultaneously protect, preserve, inform, enhance brands, and ensure safety. Innovation advances in four directions: paperisation with specialised coatings, bioplastics adoption, thinning technology, and monomaterial designs. Results include freshness preservation extended to 65 days, waste reduction from 20 per cent to 5 per cent, 35 per cent CO2 cuts, and hologram security combating the 460 billion dollar counterfeit market. With global packaging reaching 1.05 trillion dollars in 2023 and 4.6 per cent annual growth forecast through 2030, Japanese precision positions the industry advantageously, particularly across Asian markets accounting for 65 per cent of exports.
Japan-Made Supplements and Cosmetics Earn Global Trust: The Fusion of Quality Control Systems and Artisanal Techniques
Japan's supplement and cosmetics industry has achieved remarkable export growth, with shipments rising 44 per cent in 2022 to reach 33.1 billion yen. This success stems not merely from brand recognition but from a unique fusion of rigorous quality control systems and decades-old fermentation expertise. Japanese manufacturers voluntarily adopt pharmaceutical-grade standards through GMP certification, ensuring safety and consistency throughout production. The 2024 government mandate requiring GMP compliance for functional foods marks a historic turning point, positioning Japan amongst the world's most stringent regulators. Through proprietary fermentation technologies, advanced safety testing, and meticulous attention to consumer experience, Japanese firms deliver ingredients trusted by international buyers and regulatory authorities alike.
Japanese capsule shell quality control and technology
The global capsule shell market, valued at approximately 3.5 billion dollars in 2024, represents a critical yet often overlooked component in supplement and pharmaceutical businesses. Japanese manufacturers account for only 5 to 7 per cent of global production but occupy a distinctive position through technical precision and stringent quality control. Applying pharmaceutical-grade standards to health food applications, Japanese capsules offer functional design clarity, comprehensive empirical data, and complete regulatory documentation, though unit prices run 20 to 40 per cent higher than global competitors. For foreign entrepreneurs, Japanese-made capsules prove most advantageous in premium markets and applications requiring precise functionality, whilst mass-market products often benefit from cost-competitive global suppliers.
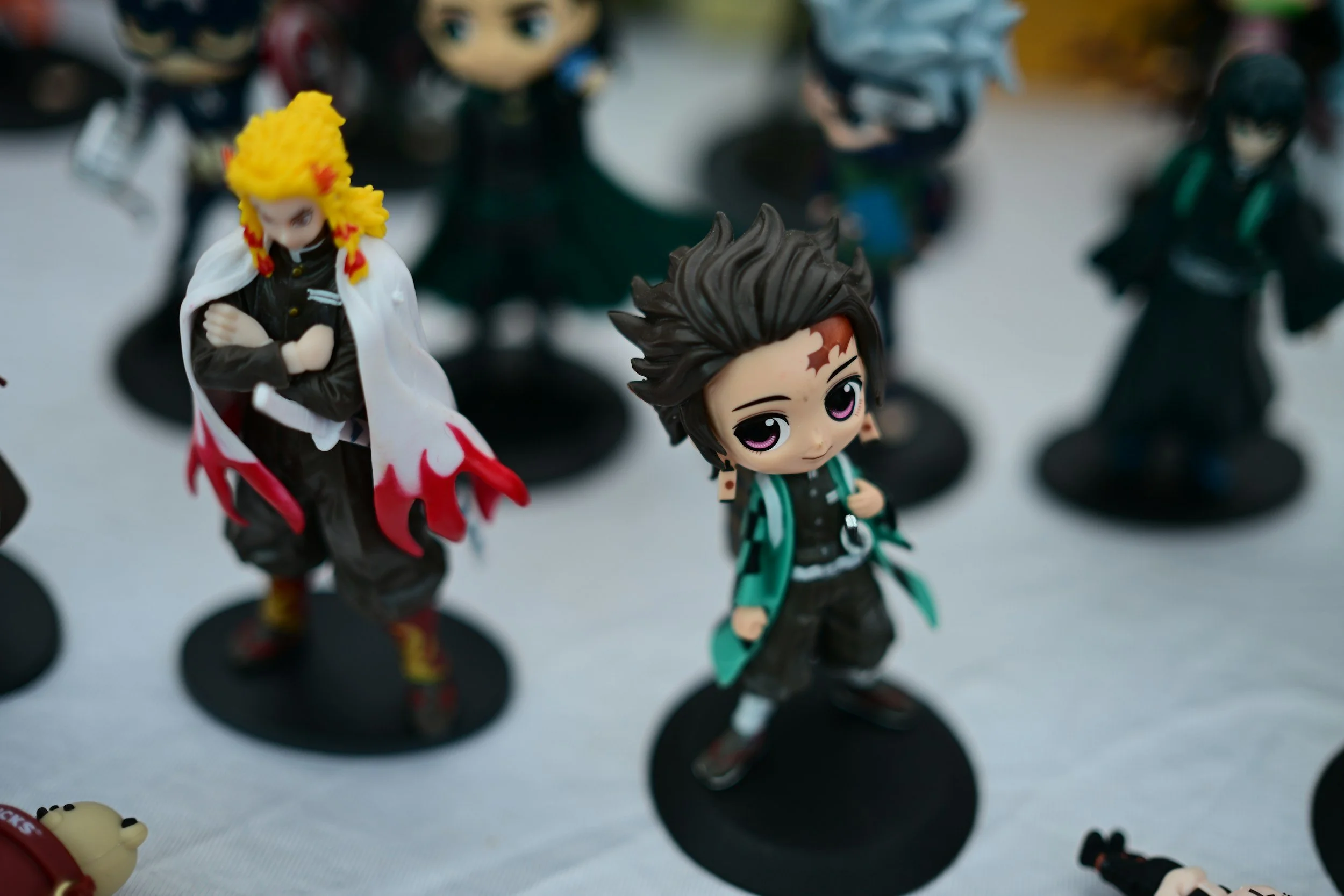
Japan's Collectors' Toy Market: An Analysis of Precision Manufacturing Technology and IP Business Models
Japan's collectors' toy market, valued at 250 billion yen domestically, represents a distinctive segment targeting adult consumers with high-quality figures priced between 20 and 500 dollars. Through precision moulding technology achieving ±0.01mm tolerances, advanced painting techniques, and preferential access to anime and manga intellectual property, Japanese manufacturers command 40 per cent of the global high-end market. These firms have built profitable niches through meticulous craftsmanship and strategic IP licensing models. However, as global demand expands at 12 per cent annually—particularly in China, North America, and South-East Asia—the industry faces critical challenges including ageing craftsmen and counterfeit products, necessitating strategic partnerships with overseas corporations to sustain growth.
Craftsmanship That Transformed Stationery: The Innovation Stories of Masking Tape, Notebooks and Fountain Pens
Japanese stationery has evolved beyond mere functional tools to become companions that inspire creativity and enhance daily life. This article explores three remarkable innovations born from Japan's manufacturing excellence: industrial masking tape transformed into a global decorative phenomenon, a notebook refined for nearly four decades to achieve a silk-like writing experience, and a century-old fountain pen nib-grinding technique revived by a master craftsman. Each story reveals a common thread—the relentless Japanese pursuit of perfection, the flexibility to reimagine existing technologies, and the irreplaceable value of human craftsmanship. From factory floors to desks worldwide, these products demonstrate how dedication to detail and user experience can turn ordinary items into cultural icons that captivate enthusiasts across the globe.
Japanese Brand Marketing: A Strategic Approach for Global Success
Japanese brands face a critical crossroads in global markets. Whilst Kobe beef remains confined to modest exports despite its 300-year heritage, Australian Wagyu dominates with a market worth 13.3 billion USD. However, sake demonstrates an alternative path—doubling exports to 2.7 billion USD in five years through unified brand protection, systematic market education, and strategic legal frameworks. This success model offers foreign companies a blueprint for collaboration: combine Japanese quality and craftsmanship with global marketing expertise and digital capabilities. Key strategies include redefining competition beyond traditional categories, extracting cultural essence whilst adapting to local contexts, implementing industry-wide protection measures, and leveraging D2C models for direct customer relationships. The opportunity lies in identifying Japanese industries with exceptional products but limited marketing prowess, then building mutually beneficial partnerships that transform "high quality but high price" into "high quality with fair pricing" through strategic market positioning.
Excellent Products, Mediocre Marketing: Why Japanese Premium Brands Lose in Overseas Markets
Japanese premium brands face a paradox: world-renowned quality yet struggling market performance overseas. Despite "Made in Japan" representing excellence in craftsmanship and precision, many Japanese products lose market share to competitors with inferior quality but superior marketing. This article examines why brands like Kobe beef, constrained by rigid quality standards and fragmented marketing, are being outpaced by Australia's flexible Wagyu industry, which dominates global markets through strategic positioning, unified branding, and digital-first approaches. By analysing real-world case studies and competitor strategies, we reveal the five critical pitfalls Japanese brands must overcome—from reactive intellectual property protection to digital marketing deficiencies—and provide actionable insights for foreign companies seeking to leverage Japan's exceptional products, technology, and talent in building truly competitive global businesses.
Japan's Character Business: How Cultural Heritage and Strategic Licensing Drive Billion-Dollar Global Success
Japan's character business has achieved remarkable global success, with iconic characters like Pokémon and Hello Kitty generating tens of billions of dollars in revenue and dominating international markets. This success stems from a unique fusion of centuries-old artistic traditions—from 12th-century Chōjū-giga to Hokusai's manga—with modern storytelling techniques pioneered by creators like Osamu Tezuka. Japan's sophisticated Production Committee System enables strategic rights management and licensing across diverse product categories, whilst cultural translatability allows these characters to resonate worldwide. Despite challenges including brand dilution risks and counterfeit products, Japanese characters continue to account for approximately 65 per cent of the global television animation market, establishing themselves as powerful international cultural and commercial brands.
Japan's Lens Technology: Competitiveness in Global Markets and Strengths of Specialised Companies
Japan's lens industry maintains a dominant position in global markets through exceptional precision manufacturing and innovative coating technologies. Japanese manufacturers achieve manufacturing precision to 1/10,000 of a millimetre with integrated domestic production, delivering high-function polarised lenses at one-third the price of equivalent German products. Notable innovations include world-first sulphur-containing urethane materials and double-sided aspherical lenses prioritising visual comfort and reduced eye fatigue. Both major manufacturers and specialised small and medium-sized enterprises contribute to Japan's technological leadership across camera equipment, medical devices, and consumer products, with export values reaching 11.914 billion yen for photographic lenses and sustained growth projected across all sectors.
What is the Production Committee System? Basic Structure and Historical Explanation for Overseas Companies
Japan's production committee system is a unique collaborative funding model that enables multiple companies—publishers, animation studios, broadcasters, and merchandisers—to jointly invest in content production whilst retaining rights within their respective domains. Unlike Western vertically integrated approaches, this system has powered Japan's rise as a global content leader, with approximately 80% of anime produced through this framework.
For overseas companies, success requires gradual market entry through low-risk partnerships, local relationship building emphasising trust and cultural understanding, and value-added propositions beyond financial investment. Key challenges include complex multi-layered rights management, consensus-driven decision-making processes, and cultural barriers such as informal consultation practices. Understanding this system represents a significant competitive advantage for companies seeking sustainable presence in Japan's lucrative content market.
The Invisible Wall: Why Japan's Unique Wholesaler System Blocks Foreign Companies from Market Entry
Japan's distinctive "tonya" wholesaler system, developed over centuries, presents both challenges and opportunities for foreign businesses seeking to enter the Japanese market. While this multi-layered distribution network may appear as a barrier to direct procurement of high-quality Japanese products, understanding its true function reveals significant advantages. The system serves as more than mere intermediation—it provides market intelligence, quality assurance, risk management, and crucial trust-building between foreign companies and Japanese manufacturers. By partnering with established wholesalers, international businesses can overcome language barriers, navigate complex regulations, and access exclusive products from traditional artisans and small manufacturers who typically avoid direct foreign transactions.
Why Japanese Fishing Tackle Manufacturers Dominate the Global Market: Technological Innovation and Market Adaptation Strategies
Japanese fishing tackle companies hold a strong position in the global market, but their influence extends well beyond fishing. The precision technologies developed for making fishing rods are now utilised in medical devices, electronics, and automotive parts. From traditional craftsmanship to modern innovation, discover how Japan's fishing tackle industry has quietly become a driving force in multiple sectors worldwide.
Japan's World-Leading Absorbent Material Technology
Japan's advanced absorbent material technologies are transforming global hygiene and medical markets through breakthrough innovations in ultra-thin, high-performance materials. Major corporations are pioneering SAP recycling systems and circular economy models, while SMEs contribute pulp-free technologies that cut thickness by half. With Japan targeting recycling implementation across 100 municipalities by 2030, the industry balances superior absorption performance with environmental sustainability, offering solutions that reduce waste, lower transport costs, and meet growing global demand for eco-conscious, high-quality materials from Japan.
Challenges in Sustainable Paper Product Development in Japan
Japanese paper manufacturers have developed advanced water-soluble toilet paper technologies driven by unique infrastructure constraints and earthquake-resistant sewage systems with smaller pipe diameters. Strict JIS standards require rapid dissolution whilst maintaining strength, achieved through precise fibre control and specialised manufacturing processes. Despite manufacturing costs being 1.5-2 times higher than in Asia, companies maintain competitiveness through technological innovation. Small and medium enterprises are driving sector advancement through regional collaboration, developing breakthrough technologies including coreless paper systems, long-length processing capabilities, and multi-colour printing on recycled materials. These innovations emphasise environmental sustainability and leverage regional manufacturing clusters to create high-value, eco-conscious solutions that differentiate Japanese products in global markets.